|
Professor Anvari Taught manufacturing and industrial systems engineering courses at the University of Michigan for five years where he received his three engineering degrees, and as an adjunct professor he teaches project and cost management at local universities in the Washington DC area.� In his early career he worked at General Motors as a production engineer and later as an operations research and systems analyst at the cost and economic analysis center in Washington DC. Mort is currently the Director of Programs and Strategy at ASA (FM&C) and the Lean Six Sigma (LSS) deployment Director where he oversees process improvement initiatives, economic studies validation, cost benefit analysis, and risk and uncertainty analysis in support of major defense programs. Mort is Defense Acquisition University Level III Certified in Business Financial Management (BFM), and Business Cost Estimating (BCE). Mort has� received several professional awards that includes the 2006 DoD modeling and simulation award. In his public lectures, Mort stimulates cost culture debates among government and industry leaders and managers. Professor Anvari has repeatedly appeared on live television programs analyzing the political economy of the Middle East. |
















|
Accounting
Accounting is the measurement, processing and communication of financial information about economic entities. Accounting, which has been called the "language of business",� measures the results of an organization's economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of users including investors, creditors, management, and regulators.� Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants.
Accounting can be divided into several fields including financial accounting, cost accounting, management accounting, auditing, and tax accounting.� Financial accounting focuses on the reporting of an organization's financial information, including the preparation of financial statements, to external users of the information, such as investors, regulators and suppliers;� and management accounting focuses on the measurement, analysis and reporting of information for internal use by management.� The recording of financial transactions, so that summaries of the financials may be presented in financial reports, is known as bookkeeping, of which double-entry bookkeeping is the most common system.
Accounting is facilitated by accounting organizations such as standard-setters, accounting firms and professional bodies. Financial statements are usually audited by accounting firms,[9] and are prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). GAAP is set by various standard-setting organizations such as the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States and the Financial Reporting Council in the United Kingdom.� As of 2012, "all major economies" have plans to converge towards or adopt the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
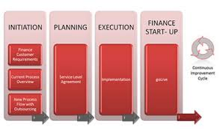
Cost accounting is a complex process of collecting, analyzing, summarizing and evaluating various alternative courses of action. Its goal is to advise the management on the most appropriate course of action based on the cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future.
Since managers are making decisions only for their own organization, there is no need for the information to be comparable to similar information from other organizations. Instead, information must be relevant for a particular environment. Cost accounting information is commonly used in financial accounting information, but first we are concentrating on its use by managers to make decisions.
Unlike the accounting systems that help in the preparation of financial reports periodically, the cost accounting systems and reports are not subject to rules and standards like the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. As a result, there is wide variety in the cost accounting systems of the different companies and sometimes even in different parts of the same company or organization.�
Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting: Financial accounting aims at finding out results of accounting year in the form of Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.� Cost Accounting aims at computing cost of production/service in a scientific manner and facilitates cost control and cost reduction.
Financial accounting reports the results and position of business to government, creditors, investors, and external parties.� Cost Accounting is an internal reporting system for an organization�s own management for decision making.
In financial accounting, cost classification based on type of transactions, e.g. salaries, repairs, insurance, stores etc.� In cost accounting, classification is basically on the basis of functions, activities, products, process and on internal planning and control and information needs of the organization.
Financial accounting aims at presenting �true and fair� view of transactions, profit and loss for a period and Statement of financial position (Balance Sheet) on a given date. It aims at computing �true and fair� view of the cost of production/services offered by the firm.
Lean accounting has developed in recent years to provide the accounting, control, and measurement methods supporting lean manufacturing and other applications of lean thinking such as healthcare, construction, insurance, banking, education, government, and other industries.
There are two main thrusts for Lean Accounting. The first is the application of lean methods to the company's accounting, control, and measurement processes. This is not different from applying lean methods to any other processes.
The objective is to eliminate waste, free up capacity, speed up the process, eliminate errors & defects, and make the process clear and understandable. The second (and more important) thrust of Lean Accounting is to fundamentally change the accounting, control, and measurement processes so they motivate lean change & improvement, provide information that is suitable for control and decision-making, provide an understanding of customer value, correctly assess the financial impact of lean improvement, and are themselves simple, visual, and low-waste. Lean Accounting does not require the traditional management accounting methods like standard costing, activity-based costing, variance reporting, cost-plus pricing, complex transactional control systems, and untimely & confusing financial reports. These are replaced by:
� lean-focused performance measurements � simple summary direct costing of the value streams � decision-making and reporting using a box score � financial reports that are timely and presented in "plain English" that everyone can understand � radical simplification and elimination of transactional control systems by eliminating the need for them � driving lean changes from a deep understanding of the value created for the customers � eliminating traditional budgeting through monthly sales, operations, and financial planning processes (SOFP) � value-based pricing � correct understanding of the financial impact of lean change.
As an organization becomes more mature with lean thinking and methods, they recognize that the combined methods of lean accounting in fact creates a lean management system (LMS) designed to provide the planning, the operational and financial reporting, and the motivation for change required to prosper the company's on-going lean transformation.
|



|
Mort Anvari |

|
Professor Anvari Taught manufacturing and industrial systems engineering courses at the University of Michigan for five years where he received his three engineering degrees, and as an adjunct professor he teaches project and cost management at local universities in the Washington DC area.� In his early career he worked at General Motors as a production engineer and later as an operations research and systems analyst at the cost and economic analysis center in Washington DC. Mort is currently the Director of Programs and Strategy at ASA (FM&C) and the Lean Six Sigma (LSS) deployment Director where he oversees process improvement initiatives, economic studies validation, cost benefit analysis, and risk and uncertainty analysis in support of major defense programs. Mort is Defense Acquisition University Level III Certified in Business Financial Management (BFM), and Business Cost Estimating (BCE). Mort has� received several professional awards that includes the 2006 DoD modeling and simulation award. In his public lectures, Mort stimulates cost culture debates among government and industry leaders and managers. Professor Anvari has repeatedly appeared on live television programs analyzing the political economy of the Middle East. |


|
|
Cost Accounting Topics |
|
|
|
1 |
Accounting Theory |
|
|
|
2 |
Advanced Accounting |
|
|
|
3 |
Financial Accounting Theory |
|
|
|
4 |
Management Accounting |
|
|
|
5 |
Financial Statements |
|
|
|
6 |
Banking Systems |
|
|
|
7 |
Business Intelligence: A Managerial Approach |
|
|
|
8 |
Cost Control |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
Accounting Theory |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Advanced Accounting |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
8 |
||
|
3 |
9 |
||
|
4 |
10 |
||
|
5 |
9 |
||
|
6 |
1 |
||
|
7 |
2 |
||
|
8 |
3 |
||
|
9 |
4 |
||
|
10 |
5 |
||
|
11 |
6 |
||
|
12 |
7 |
||
|
13 |
8 |
||
|
14 |
9 |
||
|
15 |
10 |
||
|
16 |
11 |
||
|
17 |
12 |
||
|
18 |
13 |
||
|
19 |
14 |
||
|
20 |
15 |
||
|
21 |
16 |
||
|
22 |
17 |
||
|
3 |
Financial Accounting Theory |
18 |
|
|
1 |
19 |
||
|
2 |
20 |
||
|
3 |
21 |
||
|
4 |
22 |
||
|
5 |
23 |
||
|
6 |
24 |
||
|
7 |
25 |
||
|
8 |
26 |
||
|
4 |
Management Accounting |
27 |
|
|
1 |
28 |
||
|
2 |
29 |
||
|
3 |
30 |
||
|
4 |
31 |
||
|
5 |
32 |
||
|
6 |
33 |
||
|
7 |
34 |
||
|
8 |
35 |
||
|
9 |
10 |
||
|
10 |
1 |
||
|
11 |
2 |
||
|
12 |
3 |
||
|
13 |
4 |
||
|
14 |
5 |
||
|
5 |
Financial Statements |
6 |
|
|
1 |
7 |
||
|
2 |
8 |
||
|
3 |
9 |
Problem-Solving Using Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control |
|
|
4 |
10 |
||
|
5 |
11 |
||
|
6 |
12 |
||
|
6 |
Banking Systems |
13 |
|
|
1 |
14 |
||
|
2 |
15 |
||
|
3 |
16 |
||
|
4 |
17 |
||
|
5 |
18 |
||
|
6 |
The Stock Market, Information, and Financial Market Efficiency |
19 |
|
|
7 |
20 |
||
|
8 |
21 |
||
|
9 |
Transactions Costs, Asymmetric Information, and Structure of Financial System |
22 |
|
|
10 |
23 |
||
|
11 |
Investment Banks, Mutual Funds, Hedge Funds, and Shadow Banking System |
24 |
|
|
12 |
11 |
Accounting Excel Template |
|
|
13 |
1 |
||
|
14 |
The Federal Reserve�s Balance Sheet and Money Supply Process |
2 |
|
|
15 |
3 |
||
|
16 |
4 |
||
|
17 |
Monetary Theory I: The Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Model |
5 |
|
|
18 |
6 |
||
|
7 |
Business Intelligence: A Managerial Approach |
7 |
|
|
1 |
8 |
||
|
2 |
9 |
||
|
3 |
10 |
||
|
4 |
11 |
||
|
5 |
12 |
||
|
6 |
13 |
||
|
7 |
14 |
||
|
8 |
15 |
||
|
9 |
16 |
||
|
A |
17 |
||
|
B |
18 |
||
|
8 |
Cost Control |
19 |
|
|
1 |
20 |
||
|
2 |
8 |
Cost Control (continue) |
|
|
3 |
11 |
||
|
4 |
12 |
||
|
5 |
13 |
||
|
6 |
14 |
||
|
7 |
15 |