|
Cost
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something, and hence is not available for use anymore.� In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost.� In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing.� This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production.
More generalized in the field of economics, cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process or as a differential for the result of a decision.� Hence cost is the metric used in the standard modeling paradigm applied to economic processes.� Costs are often further described based on their timing or their applicability.
When developing a business plan for a new or existing company, product, or project, planners typically make Cost Estimates in order to assess whether revenues/benefits will cover costs (see cost-benefit analysis).� This is done in both business and government.� Costs are often underestimated, resulting in cost overrun during execution.� Cost-plus pricing, is where the price equals cost plus a percentage of overhead or profit margin.
In accounting, costs are the monetary value of expenditures for supplies, services, labor, products, equipment and other items purchased for use by a business or other accounting entity. It is the amount denoted on invoices as the price and recorded in bookkeeping records as an expense or asset cost basis.
Opportunity Cost, also referred to as economic cost is the value of the best alternative that was not chosen in order to pursue the current endeavor�i.e., what could have been accomplished with the resources expended in the undertaking. It represents opportunities forgone.� In theoretical economics, cost used without qualification often means opportunity cost.
Classification of costs:� Classification of cost means, the grouping of costs according to their common characteristics. The important ways of classification of costs are:
� By Element: There are three elements of costing i.e. material, labor and expenses. � By Nature or Traceability: Direct Costs and Indirect Costs. Direct Costs are Directly attributable/traceable to Cost Object. Direct costs are assigned to Cost Object. Indirect Costs are not directly attributable (traceable) to Cost Object. Indirect costs are allocated or apportioned to cost objects. � By Functions: production, administration, selling and distribution, R&D. � By Behavior: fixed, variable, semi-variable. Costs are classified according to their behavior in relation to change in relation to production volume within given period of time. Fixed Costs remain fixed irrespective of changes in the production volume in given period of time. Variable costs change according to volume of production. Semi-variable Costs are partly fixed and partly variable. � By control ability: controllable, uncontrollable costs. Controllable costs are those which can be controlled or influenced by a conscious management action. Uncontrollable costs cannot be controlled or influenced by a conscious management action. � By normality: normal costs and abnormal costs. Normal costs arise during routine day-to-day business operations. Abnormal costs arise because of any abnormal activity or event not part of routine business operations. E.g. costs arising of floods, riots, accidents etc. � By Time: Historical Costs and Predetermined costs. Historical costs re costs incurred in the past. Predetermined costs are computed in advance on basis of factors affecting cost elements. Example: Standard Costs. � By Decision making Costs: These costs are used for managerial decision making. � Marginal Costs: Marginal cost is the change in the aggregate costs due to change in the volume of output by one unit. � Differential Costs: This cost is the difference in total cost that will arise from the selection of one alternative to the other. � Opportunity Costs: It is the value of benefit sacrificed in favor of an alternative course of action. � Relevant Cost: The relevant cost is a cost which is relevant in various decisions of management. � Replacement Cost: This cost is the cost at which existing items of material or fixed assets can be replaced. Thus this is the cost of replacing existing assets at present or at a future date. � Shutdown Cost: These costs are the costs which are incurred if the operations are shut down and they will disappear if the operations are continued. � Capacity Cost: These costs are normally fixed costs. The cost incurred by a company for providing production, administration and selling and distribution capabilities in order to perform various functions. Other Costs: Marginal costing (Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis and Marginal cost)� The cost-volume-profit analysis is the systematic examination of the relationship between selling prices, sales, production volumes, costs, expenses and profits. This analysis provides very useful information for decision-making in the management of a company. For example, the analysis can be used in establishing sales prices, in the product mix selection to sell, in the decision to choose marketing strategies, and in the analysis of the impact on profits by changes in costs. In the current environment of business, a business administration must act and take decisions in a fast and accurate manner. As a result, the importance of cost-volume-profit is still increasing as time passes. |
|
The course materials listed on this web site are copy rights � by the subject authors and publishers. They are solely intended for classroom teaching and online reference. Copy and/or redistribution of these contents are prohibited by the US copyright law. |



|
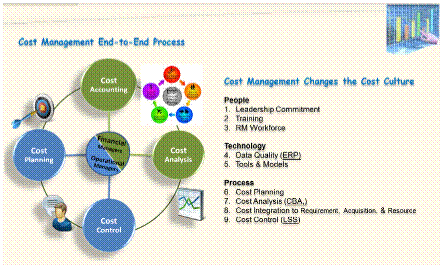
Cost management
Cost management is the process by which companies control and plan the costs of doing business. Individual projects should have customized plans for this process, and companies as a whole also integrate cost management into their overall business model. There is no single accepted definition for this term, because it has such broad applications and possible strategies. When properly implemented, this process will translate into reduced costs of production for products and services, as well as increased value being delivered to the customer.
For a company's management to be effective overall, cost management must be an integral feature of it. It is easiest to understand this concept if it is explained in the context of a single project. For instance, before a project is started, the anticipated costs should be identified and measured. These expenses should then be approved before any purchasing occurs. During the process of completing a project, all incurred costs should be noted and kept in a record of some kind, to help ensure that the costs are controlled and kept in line with initial expectations, to the extent that this is possible.
Taking this approach to cost management will help a company determine whether they accurately estimated expenses at first, and will help them more closely predict expenses in the future. Any overspending can also be monitored in this way, and either eliminated in future projects or specifically approved if the expense was necessary. Cost management cannot be used in isolation; projects must be organized and tailored with this strategy in mind.
Starting a project with cost management in mind will help to avoid certain pitfalls that may be present otherwise. If the objectives of the project are not clearly defined at first, or are changed during the course of the project, cost over-runs will be more likely. If costs are not fully researched before the project, they may be underestimated, thereby inflating the expectation of the project's success unrealistically. Construction projects are subject to their own particular challenges; these can include constraints in the form of laws and regulations that must be planned around.
If the project is completely and clearly defined, this will facilitate effective management of the costs it will incur. Effective cost management strategies will help a team deliver a finished project within the allocated budget, while also making it as valuable as possible to the company. There is always the possibility of unexpected costs, but preparation in the form of cost management will likely make them much easier to deal with when they occur.
Related Topics � Business Strategy � Quality Control � Budget Software � Business Plan Preparation � Project Management � Software Cost Control � Budget Form � Well Control � Business Process Software
|