|
Acquisition
Acquisition is the procurement of goods, services or works from an outside external source.� It is favorable that the goods, services or works are appropriate and that they are procured at the best possible cost and schedule to meet the needs of the purchaser in terms of quality and quantity, time, and location.� Corporations and public bodies often define processes intended to promote fair and open competition for their business while minimizing exposure to fraud and collusion.
Almost all Acquisition decisions include factors such as delivery and handling, marginal benefit, and price fluctuations. Acquisition generally involves making buying decisions under conditions of scarcity.� If good data is available, it is good practice to make use of economic analysis methods such as cost-benefit analysis or cost-utility analysis. An important distinction should be made between analyses without risk and those with risk. Where risk is involved, either in the costs or the benefits, the concept of expected value may be employed.
The US Defense Acquisition University (DAU) defines procurement as the act of buying goods and services for the government.� DAU defines acquisition as the conceptualization, initiation, design, development, test, contracting, production, deployment, Logistics Support (LS), modification, and disposal of weapons and other systems, supplies, or services (including construction) to satisfy Department of Defense needs, intended for use in or in support of military missions.
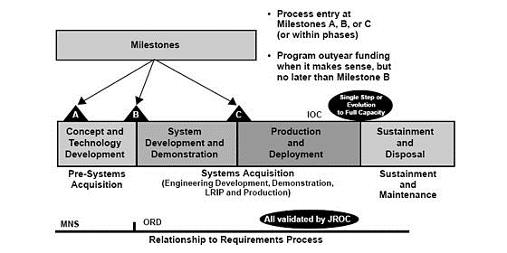
Acquisition is therefore a much wider concept than procurement, covering the whole life cycle cost of acquired systems. Multiple acquisition models or acquisition process exists, one of which is the revised acquisition process for major systems in industry and defense.� The process is defined by a series of phases during which technology is defined and matured into viable concepts, which are subsequently developed and readied for production, after which the systems produced are supported in the field.
Acquisition Process, Generally, federal acquisitions begin with identification of a requirement by a specific federal activity. A basic idea of what is needed and the problem statement is prepared and the requiring activity meets with an acquisition command having a Contracting Officer with an appropriate warrant issued by a specific acquisition activity.
�
Contracting � Business process outsourcing (BPO) is a subset of outsourcing that involves the contracting of the operations and responsibilities of specific business functions (or processes) to a third-party service provider.� Originally, this was associated with manufacturing firms that outsourced large segments of its supply chain.
BPO is typically categorized into back office outsourcing, which includes internal business functions such as human resources or finance and accounting, and front office outsourcing, which includes customer-related services such as contact center services. Often the business processes are information technology-based, and are referred to as Information Technology Enabled Service.� Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) and legal process outsourcing (LPO) are some of the sub-segments of business process outsourcing industry.
Government Contracting is the process by which the federal government acquires goods, services (notably construction), and interests in real property. Contracts for government procurement usually involve appropriated funds spent on supplies, services, and interests in real property by and for the use of the Federal Government through purchase or lease, whether the supplies, services, or interests are already in existence or must be created, developed, demonstrated, and evaluated.� ("Acquisition" defined, as to goods and services only). Federal Government contracting has the same legal elements as contracting between private parties: a lawful purpose, competent contracting parties, an offer, an acceptance that complies with the terms of the offer, mutuality of obligation, and consideration. However, Federal contracts are much more heavily regulated, subject to volumes of statutes dealing with Federal contracts and the Federal contracting process, mostly in Titles 10, 31, 40, and 41 of the United States Code.
|


|
The course materials listed on this web site are copy rights � by the subject authors and publishers. They are solely intended for classroom teaching and online reference. Copy and/or redistribution of these contents are prohibited by the US copyright law. |